Multimodal Interaction
In the Networked Presentations section we have shown how MindXpres instances can form networks and how hardware can be integrated in the network for usage in combination with the running presentation. Other that audience-oriented functionality the same mechanism offers opportunities to integrate hardware for presenter interaction. Current tools often focus on using the keyboard or the mouse, but MindXpres' plug-in architecture allows developers to create all kinds of software or hardware solutions for interacting with the presentation. Implemented examples include, but are not limited to:
- Dedicated customisable presenter views running on a smartphone or tablet
- Gesture-based interaction via the Microsoft Kinect or Mio Gesture Armband
- Navigation based on laserpoint tracking on the projection screen
- Annotating slides by drawing on a mobile device or by using digital pens (e.g. LiveScribe)
Relevant Publications
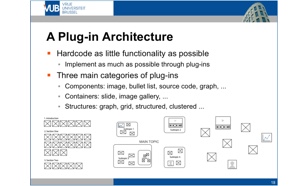
Feature Overview

MindXpres presentations can not only connect to each other but all kinds of hardware can be integrated in the network for navigation, interaction or audience participation. Examples include customised presenter interfaces running on a mobile device, clickers for audience input or specialised hardware for gesture or voice recognition.

MindXpres generates presentations based on web technologies allowing them to run offline or online, on both computers and mobile devices without the need to install any software. Furthermore, presentations can easily be put online and viewers can replay the presentation as it was given, or explore the presentation by themselves.